Transformer-based Tooth Alignment Prediction with Occlusion and Collision Constraints
Published in ICCV, 2025
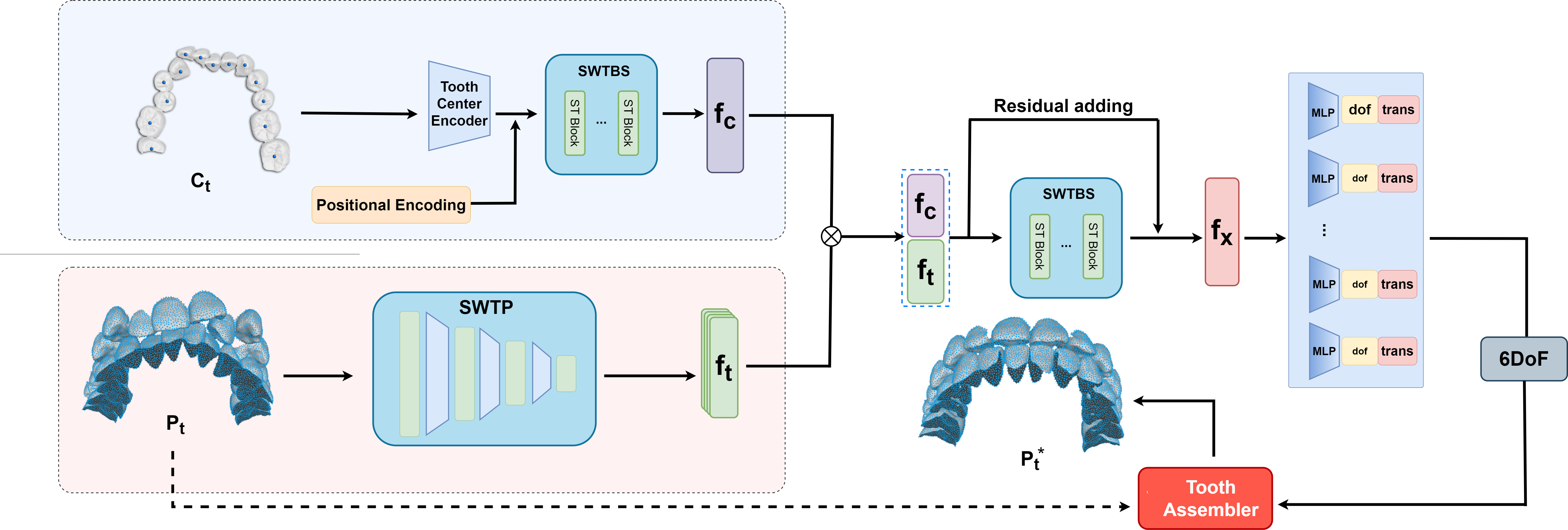
Figure 1: Network architecture overview. The encoding module has two branches: one for global features from the tooth center and one for local features from the tooth point cloud. Global features are extracted using SWTBS with shared Swin-T blocks, while local features are processed via SWTP with multi-stage hierarchical fusion. The features are merged, passed through SWTBS propagation, and then regressed by an MLP to predict the 6DOF transformation parameters for orthodontics.
Source Code STTAlign can be found in Github.
Dataset TeethAlign3D can be found here and downloaded in Zenodo.
Abstract: The planning of digital orthodontic treatment requires providing tooth alignment, which relays clinical experiences heavily and consumes a lot of time and labor to determine manually. In this work, we proposed an automatic tooth alignment neural network based on Swin-transformer. We first re-organized 3D point clouds based on dental arch lines and converted them into order-sorted multi-channel textures, improving both accuracy and efficiency. We then designed two new orthodontic loss functions that quantitatively evaluate the occlusal relationship between the upper and lower jaws. They are important clinical constraints, first introduced and lead to cutting-edge prediction accuracy. To train our network, we collected a large digital orthodontic dataset in more than 2 years, including various complex clinical cases. We will release this dataset after the paper’s publishment and believe it will benefit the community. Furthermore, we proposed two new orthodontic dataset augmentation methods considering tooth spatial distribution and occlusion. We compared our method with most SOTA methods using this dataset, and extensive ablation studies and experiments demonstrated the high accuracy and efficiency of our method.
We designed a serialization method based on a simulated dental arch line, created by fitting central points from a tooth segmentation model and connecting them with Hermite curves. Points are sorted by their distance from the arch, with labial points positive and lingual points negative. Regular data augmentation applies random rotation and translation on teeth based on a Gaussian distribution. It generates pre-orthodontic data while preserving the ground truth as post-orthodontic data. However, regular augmentation may produce clinical-illogical cases, including too far away from the arch lines and teeth collision. For this sake, we propose a constrained data augmentation that involves two relevant clinical constraints: jaw regularization constraints and collision detection constraints.
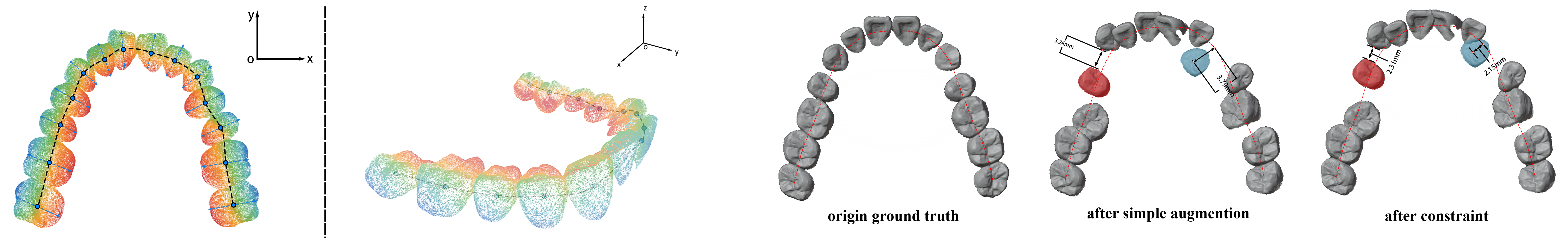
Figure 2: Left: Points cloud are serialized according to their distance from simulated dental arch line, values on lingual side set as positive while labial side set as negative. Right: The maxillofacial regularization corrects excessive gaps or deviations based on dataset statistics.
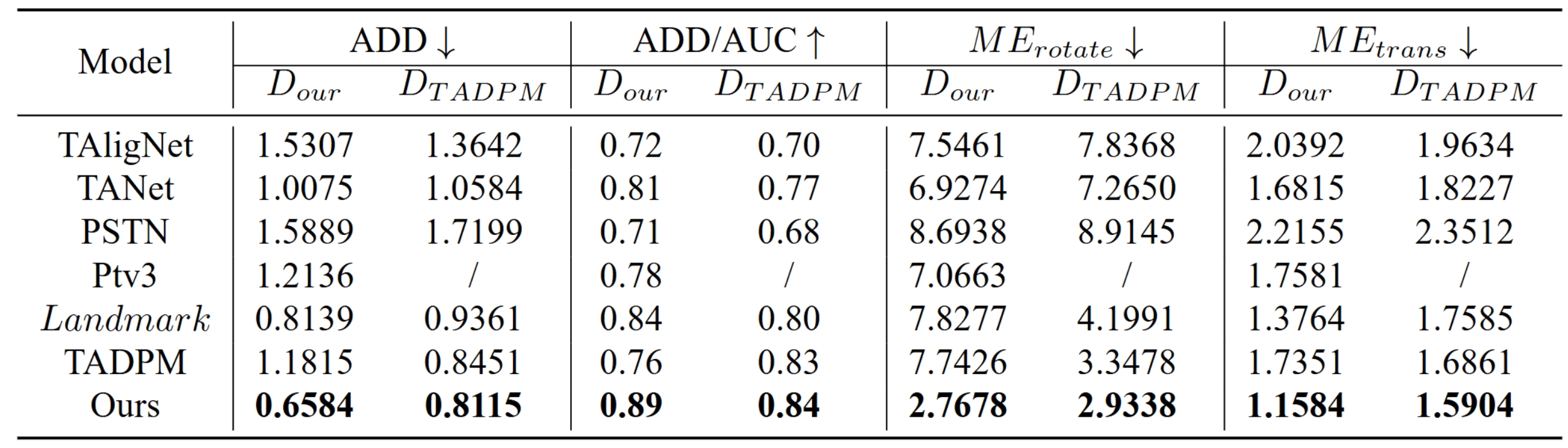
Table 1: Comparison of evaluation metrics between the proposed method and the SOTA method.
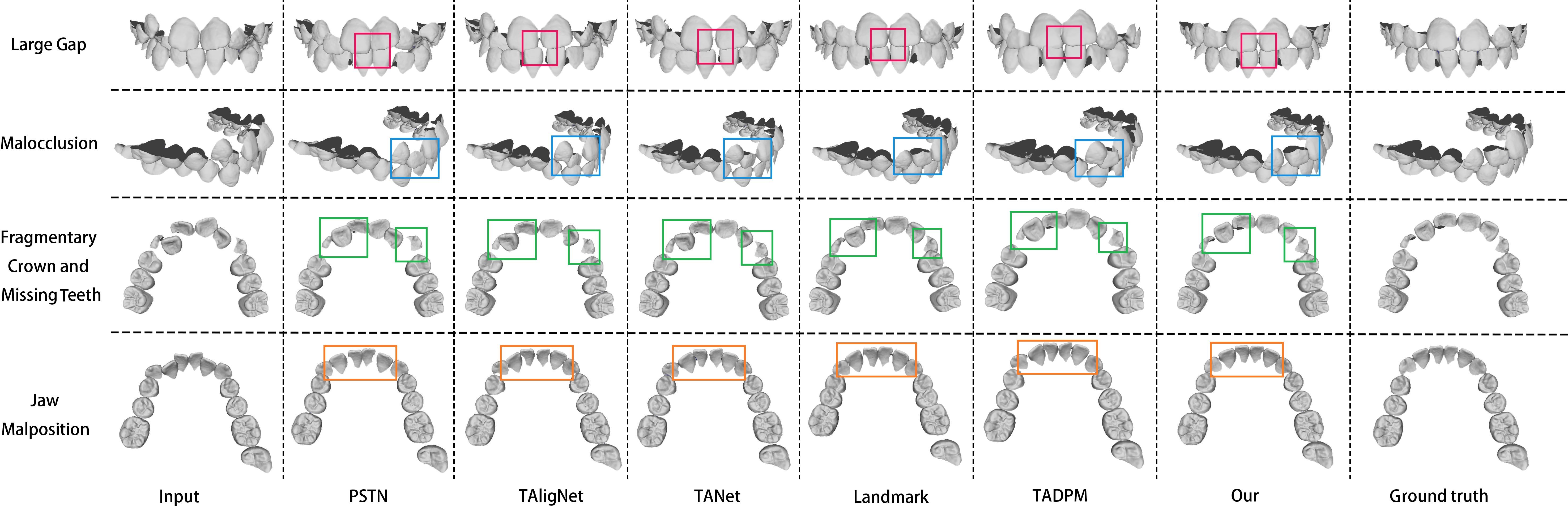
Figure 3: Comparison of prediction results between the proposed method and other methods. Here, four typical and challenging orthodontic problems are selected, listed from top to bottom: large gap, malocclusion, fragmentary crown and missing teeth, and jaw malposition.
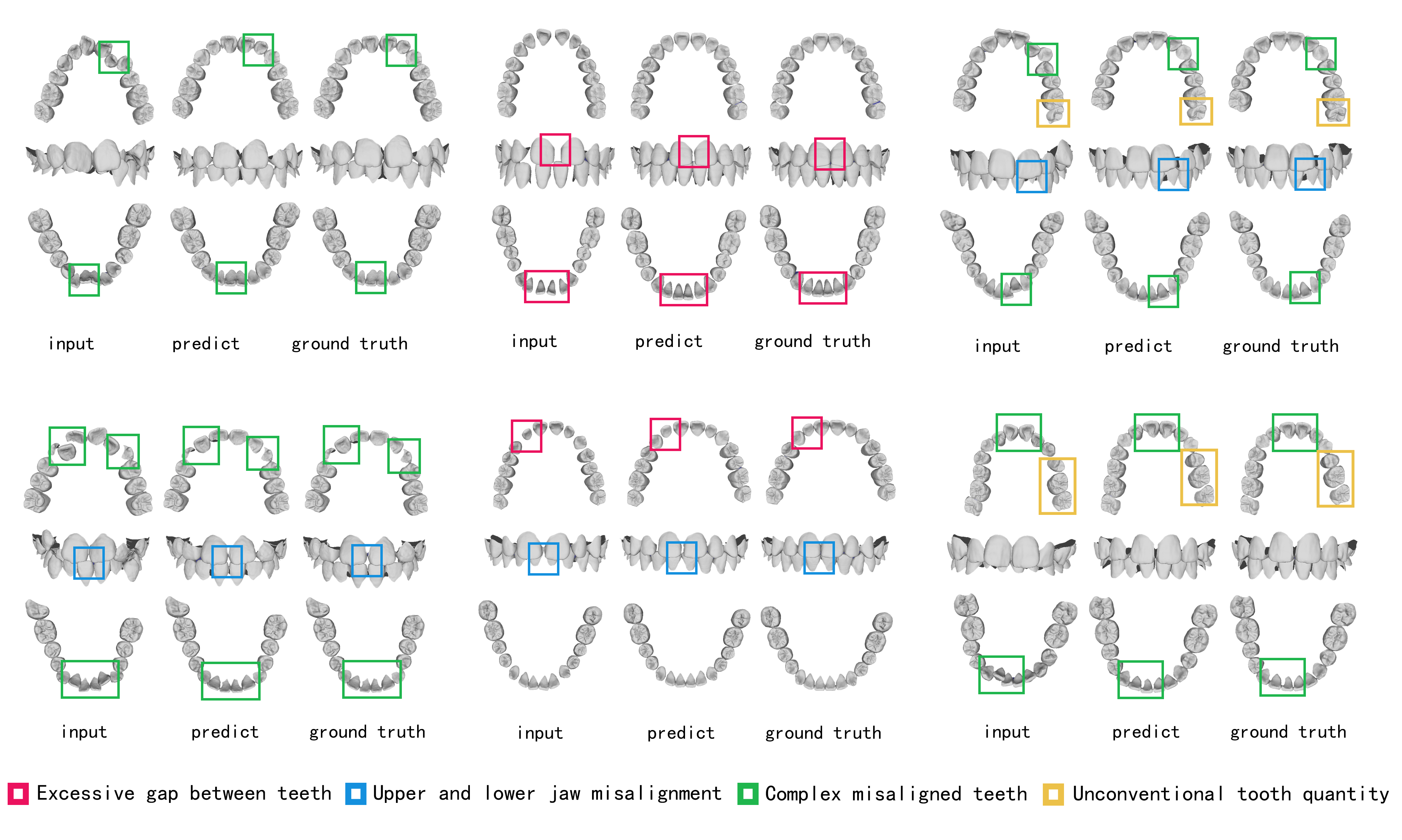
Figure 4 shows the alignment prediction results of our method on 6 data cases. Cases 1/3/4/6 have missing teeth.
Recommended citation: Zhenxing Dong, Jiazhou Chen. " Transformer-based Tooth Alignment Prediction with Occlusion and Collision Constraints." ICCV. 2025.
